IF Statements
Logical IF statement
IF statements execute conditional instructions. These statements make the program naughty. For every single task, it sets one condition in advance. If a particularly given condition (given by logical_expression) holds true, then only the program will execute a given statement (executable_statement).
IF (logical_expression) executable_statement
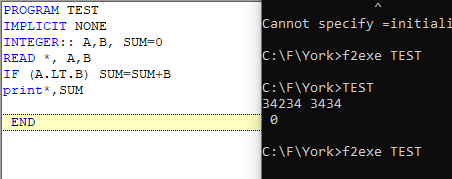
Block IF statement
The naughtiness of the program increases here. It says if this, then I will do this work, if not this, I will do that work and so one. So, the work it does depends upon the type of bribe. In this statement, optional one or multiple ELSE IF block follows a logical IF block.
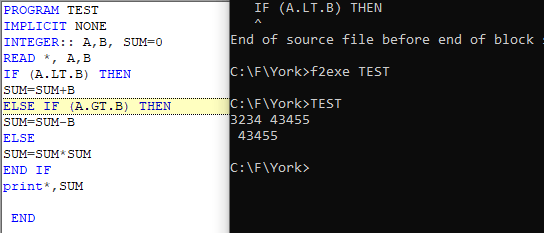
GOTO Statements
GOTO statement causes the execution to jump to a labeled statement and resume the execution from there.
GOTO label
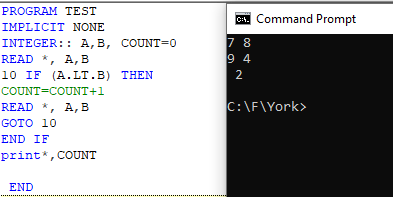
DO loops
It is a sequence of statements beginning with a DO statement. This loop allows giving the same set of instructions to a number of variables within a single go. This makes the program short and concise. The structure of a DO statement is as follows:
DO label, Variable = e1, e2, e3
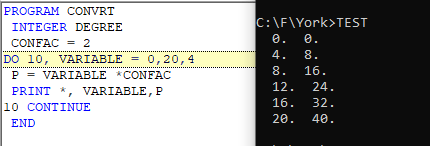
e1 is the starting variable, e2 is the ending variable and e3 is the spacing between two variables. For example, to use variables from 1 to 100 with a spacing of 5, we write
DO 10 VARIABLE = 1, 100, 5
However, e3 is optional. the label is the integer-valued label of continue command.
No Responses